信号的捕获与同步
在前面的学习当中已经完成了信号的搜索,通过信号的搜索,可以看到在不同频率,不同码相位下如何对输入的卫星信号进行搜索。
在之前只介绍了频率和码相位的搜索,并且并没有得到具体的频率和码相位,只是在图上显示除了对应的相关峰的分布。
其实在之前的频率,PN码搜索之后,还有一步就是卫星组合的搜索,在北斗卫星导航当中,不同的卫星组合所产生的PN码是不相同的,因此在实际的接收机当中,可能还需要一个穷举卫星组合的方式来产生具体的PN码。
关于卫星组合搜索,联合前面的频率搜索,码相位搜索的综合matlab仿真代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188clc;
close all;
clear all;
%% parameter define
PN_INDEX1 = 2 ; % choose satellites
PN_INDEX2 = 10; % choose satellites
SAMP_RATE = 8.184e6; % sample rate
CODE_RATE = 2.046e6; % standard PN code rate 2.046M
NH_CODE_LEN = 20; % the length of NH code is 20bit
SOURCE_DATA_LEN = 300; % the source data num
PN_CODE_LEN = 2046; % standard PN cod length 2046
PN_SAMP_LEN = (SAMP_RATE/CODE_RATE) * PN_CODE_LEN * NH_CODE_LEN * SOURCE_DATA_LEN; % total pn sample for data to be send
%% generate bpsk modulation data
% source_data ==> NH mod ==> PN mod ==> BPSK mod
% generate source data
source_data = rand(1, SOURCE_DATA_LEN); % generate test source data
source_data(source_data < 0.5) = -1;
source_data(source_data >= 0.5) = 1;
source_data = repelem(source_data, 1, NH_CODE_LEN); % upsample D1 signal source data to NH code modulated rate 1Kbps
% NH code
nh_code = [0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0];
nh_code = repmat(nh_code, 1, SOURCE_DATA_LEN);
nh_code(nh_code == 0) = -1;
% NH code modulation
nh_mod = source_data .* nh_code; % using .* instead of xor
% upsample to sample rata
nh_mod = repelem(nh_mod, 1, (SAMP_RATE/CODE_RATE)*PN_CODE_LEN);
% generate PN code & PN sample
[pn_code, pn_code_sample] = PNCode_Gen(PN_CODE_LEN, PN_SAMP_LEN, CODE_RATE, SAMP_RATE, PN_INDEX1);
% PN code modulation
pn_mod = nh_mod .* pn_code_sample; % using .* instead of xor
% generate carrier wave
AMP = 1;
ROM_DEPTH = 4096;
CARRIER_FREQ = CODE_RATE; % carrier frequency
FREQ_CTRL_WORLD = CARRIER_FREQ * 2^32/ SAMP_RATE;
rom_addr = 0: 1/ROM_DEPTH: 1-1/ROM_DEPTH;
carrier_wave_cos = AMP*cos(2*pi*rom_addr);
carrier_wave_sin = AMP*sin(2*pi*rom_addr);
% bpsk modulation
bpsk_mod = zeros(1,PN_SAMP_LEN);
rom_index = 1;
phase_accumulator = 0;
for i=1:PN_SAMP_LEN
%bpsk modulation
if(pn_mod(i) == -1)
bpsk_mod(i) = -carrier_wave_cos(rom_index);
else
bpsk_mod(i) = carrier_wave_cos(rom_index);
end
phase_accumulator = phase_accumulator + FREQ_CTRL_WORLD;
if(phase_accumulator > 2^32)
phase_accumulator = phase_accumulator - 2^32;
end
rom_index = round(phase_accumulator/2^20);
if(rom_index == 0)
rom_index = 1;
end
end
% plot the bpsk result
figure(1);
plot(1:1024, bpsk_mod(1:1024), 'r', 1:1024, pn_mod(1:1024),'b');
axis([0, 1024, -2, 2]);
legend('bpsk mod', 'pn mod');
title("BPSK modulation");
%% PN code capture
DATA_OFFSET = 1022;
data_in = bpsk_mod(DATA_OFFSET: end); % input bpsk data offset
FREQ_WIDTH = 15e3; % frequency search range 15kHz
FREQ_STEP = 500; % frequency search step 500Hz
FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE = round(FREQ_WIDTH/FREQ_STEP); % frequency search range
SAMP_PER_PN = round((SAMP_RATE/CODE_RATE)*PN_CODE_LEN); % for 1 complete PN code sample length
HALF_CODE_WIDTH = round((SAMP_RATE/CODE_RATE)/2); % half code offset
PN_SEARCH_RANGE = round(SAMP_PER_PN/HALF_CODE_WIDTH); % the total search range for pn code capture
% the power of correlation result
power_pre = zeros(FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE, PN_SEARCH_RANGE);
power_middle = zeros(FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE, PN_SEARCH_RANGE);
power_post = zeros(FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE, PN_SEARCH_RANGE);
SATELLITE_SEARCH_RANGE= 32;
%% satellite search
for satellite_index=1:SATELLITE_SEARCH_RANGE
%% frequency search
for freq_index=1:FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE
% generate PN code
[pn_code, pn_code_sample] = PNCode_Gen(PN_CODE_LEN, SAMP_PER_PN, CODE_RATE, SAMP_RATE, satellite_index); % generate different prn code with satellite index
pn_pre = [pn_code_sample(HALF_CODE_WIDTH+1:end), pn_code_sample(1:HALF_CODE_WIDTH)];
pn_middle = pn_code_sample;
pn_post =[pn_code_sample(SAMP_PER_PN-HALF_CODE_WIDTH+1:end), pn_code_sample(1:SAMP_PER_PN-HALF_CODE_WIDTH)];
% generate carrier wave
sin_carrier = zeros(1, SAMP_PER_PN);
cos_carrier = zeros(1, SAMP_PER_PN);
rom_index = 1;
phase_accumulator = 0;
% receiver frequency control word
rx_freq_ctrl_world = round((CARRIER_FREQ + (FREQ_STEP*freq_index - FREQ_WIDTH/2))* 2^32/ SAMP_RATE);
for i=1:SAMP_PER_PN
sin_carrier(i) = carrier_wave_sin(rom_index);
cos_carrier(i) = carrier_wave_cos(rom_index);
phase_accumulator = phase_accumulator + rx_freq_ctrl_world;
if(phase_accumulator > 2^32)
phase_accumulator = phase_accumulator - 2^32;
end
rom_index = round(phase_accumulator/2^20);
if(rom_index == 0)
rom_index = 1;
end
end
signal = data_in(1: SAMP_PER_PN);
sample_offset = 0;
% find correlation peak
for code_index = 1: PN_SEARCH_RANGE
i_data = signal .* cos_carrier;
q_data = signal .* sin_carrier;
% do correlation
temp_pre_i = sum(i_data .* pn_pre);
temp_middle_i = sum(i_data .* pn_middle);
temp_post_i = sum(i_data .* pn_post);
temp_pre_q = sum(q_data .* pn_pre);
temp_middle_q = sum(q_data .* pn_middle);
temp_post_q = sum(q_data .* pn_post);
% calculate the power
power_pre(freq_index, code_index) = temp_pre_i^2 + temp_pre_q^2;
power_middle(freq_index, code_index) = temp_middle_i^2 + temp_middle_q^2;
power_post(freq_index, code_index) = temp_post_i^2 + temp_post_q^2;
% sample_offset = sample_offset + SAMP_PER_PN + HALF_CODE_WIDTH;
% signal = data_in(sample_offset+1:sample_offset+SAMP_PER_PN);
% get nex data sample
sample_offset = sample_offset + SAMP_PER_PN;
signal = data_in(sample_offset+1: sample_offset+SAMP_PER_PN);
% shift the pn code with half code width to search for the code phase
pn_pre = [pn_pre(HALF_CODE_WIDTH+1:end), pn_pre(1:HALF_CODE_WIDTH)];
pn_middle = [pn_middle(HALF_CODE_WIDTH+1:end), pn_middle(1:HALF_CODE_WIDTH)];
pn_post = [pn_post(HALF_CODE_WIDTH+1:end), pn_post(1:HALF_CODE_WIDTH)];
end
end
% TODO: find the maximum power and frequency
[max_power, freq_pos] = max(max(power_middle, [], 2)); % this will find the max power and the corresponding frequency index
[max_power, code_phase_pos] = max(power_middle(freq_pos, :)); % this will find the max power and the corresponding code phase index
code_phase_pre = code_phase_pos - HALF_CODE_WIDTH; % the pre code phase index
code_phase_post = code_phase_pos + HALF_CODE_WIDTH; % the post code phase index
temp_power = power_middle(freq_pos, :);
if (code_phase_pre < 1)
temp_power(1: code_phase_pos) = 0;
elseif (code_phase_post > SAMP_PER_PN)
temp_power(code_phase_pre: SAMP_PER_PN) = 0;
else
temp_power(code_phase_pre: code_phase_post) = 0;
end
[second_max_power, second_code_phase_pos] = max(temp_power);
if (max_power/second_max_power > 2.5)
fprintf('%02d', satellite_index);
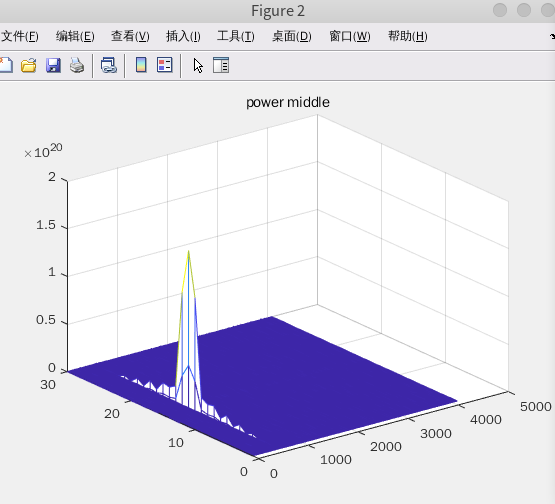
figure;mesh(1:PN_SEARCH_RANGE, 1:FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE, power_pre );title('power pre');
figure;mesh(1:PN_SEARCH_RANGE, 1:FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE, power_middle);title('power middle');
figure;mesh(1:PN_SEARCH_RANGE, 1:FREQ_SEARCH_RANGE, power_post);title('power post');
else
fprintf('.');
end
end
信号的捕获和同步
前面对之前没有实现的信号的捕获的实现的具体过程进行了一个补充,在有了前面捕获的过程之后,接下来就可以把前面捕获到的信号送入到前面学习到的PLL当中了,对载波的频率和相位进行进一步的跟踪,完成本地的想干解调。
在信号捕获阶完成之后,从捕获之后的采样点进行后一步的处理,在也即是对PLL的处理。
1 | clc; |